Nestled in the North Atlantic Ocean, Iceland is a place where volcanoes and glaciers coexist, where tourists are mesmerized by the northern lights and midnight sun, and where progressive social policies coexist with long-standing customs. Though small in population, Iceland punches well above its weight in global reputation—whether in environmental stewardship, gender equality, or quality of life.
Iceland captivates with its stark contrasts: volcanic landscapes meet glacial expanses, and the midnight sun illuminates summer nights while winter unveils the mesmerizing Northern Lights. Known as the “Land of Fire and Ice,” this island nation of 370,000 people blends raw natural beauty with a forward-thinking society. Let’s explore Iceland’s climate, economy, culture, policies, and more.
Geography and Climate
Just below the Arctic Circle lies the Nordic island nation of Iceland. At 103,000 square kilometers, it is about the size of Kentucky or South Korea. Despite its name implying that it is entirely covered in ice, Iceland is surprisingly green in the summer. It boasts dramatic natural landscapes including:
- Volcanoes and Lava Fields: Iceland is one of the most volcanically active places on Earth. The nation is situated on top of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is the meeting point of the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates. Famous volcanoes include E犀利士 yjafjallajökull and Hekla.
- Glaciers and Ice Caps: About 11% of Iceland is covered by glaciers. Vatnajökull is the largest glacier in Europe.
- Hot Springs and Geysers: Geothermal energy is abundant, and the famous Blue Lagoon and Geysir hot spring are major attractions.
Weather and Climate: A Dance of Extremes
Iceland has an oceanic or subarctic climate, with the Gulf Stream having a major impact. Contrary to what many expect, it’s not brutally cold—especially on the coasts.
Iceland’s subarctic climate is tempered by the Gulf Stream, yielding milder winters than its latitude suggests. Reykjavik averages -1°C (30°F) in winter and 12°C (54°F) in summer. Yet, the weather is famously unpredictable—sunshine, rain, and wind can cycle within hours.
- Seasonal Wonders: Experience 24-hour daylight in June (midnight sun) and near-darkness in December (polar nights).
- Storms and Winds: Winter brings fierce storms, especially in the north, while the south remains relatively sheltered.
- Travel Tips: Layer clothing year-round! Waterproof gear is essential for exploring waterfalls like Gullfoss or black-sand beaches.
- Winter: Average temperatures in Reykjavik range from -1°C to 4°C (30°F to 39°F).
- Summer: Temperatures are mild, averaging 10°C to 15°C (50°F to 59°F).
- Variations in Daylight: During Iceland’s summer, the “Midnight Sun” shines for almost twenty-four hours. In the south, daylight only lasts four to five hours during the winter.
People and Society
Iceland has a small population—about 375,000 people as of 2025. Reykjavik, the world’s northernmost capital, is home to about two-thirds of the population.
People and Culture: Literary Giants and Equality Champions
Icelanders are among the world’s most literate populations, with a deep-rooted love for storytelling.
- Cultural Highlights:
- Literary Heritage: The medieval sagas and modern authors like Halldór Laxness (Nobel laureate) thrive here. The Jolabokaflod tradition sees books exchanged on Christmas Eve.
- Music and Arts: Björk, Sigur Rós, and festivals like Iceland Airwaves put the nation on the global music map.
- Gender Equality: First to elect a female president (Vigdís Finnbogadóttir, 1980), with women holding 48% of parliament seats. LGBTQ+ rights are celebrated, including same-sex marriage since 2010.
- Language: Icelandic, a Viking-era tongue, remains largely unchanged. English is widely spoken, fostering global connectivity.
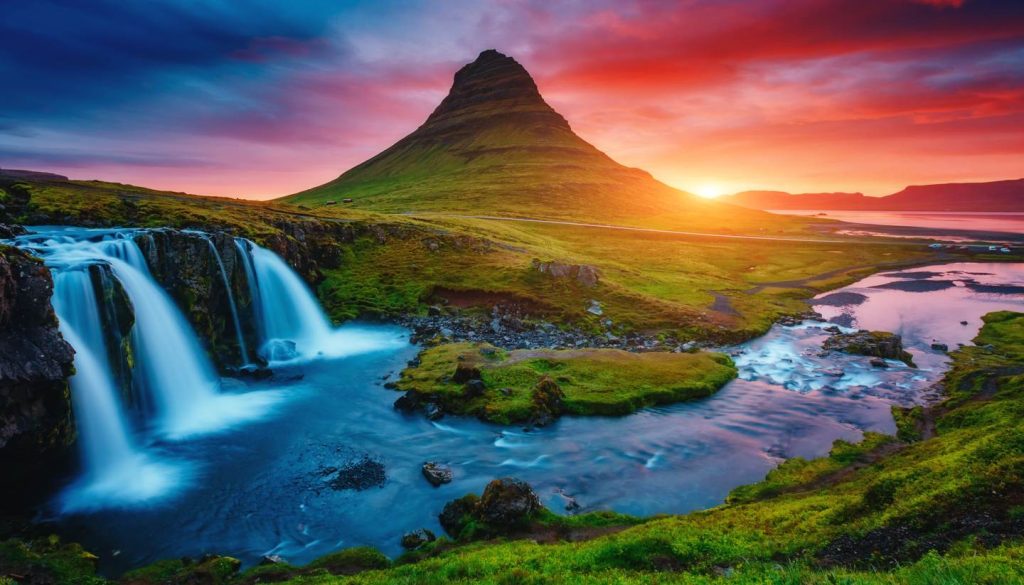

Demographics
- Ethnicity: Predominantly Icelandic (of Norse and Gaelic origin).
- Language: Icelandic, a North Germanic language that has changed very little since medieval times.
- Religion: The Evangelical Lutheran Church of Iceland is the state religion, but the society is highly secular.
Culture and Identity
Icelanders take pride in their literary history, dating back to the medieval Icelandic sagas—epic tales of heroes, settlers, and mythical creatures. Modern Iceland is deeply artistic, producing globally known musicians like Björk and bands like Sigur Rós.
- Naming System: Iceland uses a patronymic naming system, meaning people are often identified as the son or daughter of their parent (e.g., Jónsson or Jónsdóttir).
- Education: Highly valued and publicly funded. Literacy is nearly universal.
- Gender Equality: According to the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Report, Iceland routinely ranks first. Top positions in academia, business, and government are occupied by women.
Wealth and Economy
The GDP per capita of Iceland is among the highest in the world. It’s a high-income economy with a strong welfare state and a high standard of living.
Economy and Wealth: Resilience and Innovation
Despite its small population, Iceland boasts a GDP per capita of ~$70,000 (2023), driven by tourism, fishing, and renewable energy.
- Key Industries:
- Tourism: Contributed 8-10% of GDP pre-pandemic, with attractions like the Blue Lagoon drawing over 2 million visitors annually.
- Fishing: Accounts for 40% of exports, leveraging sustainable practices to protect cod and haddock stocks.
- Renewables: 85% of energy comes from geothermal and hydroelectric sources, powering industries and homes.
- Economic Resilience: After the 2008 financial crisis (which collapsed its banking sector), Iceland recovered through tourism growth, capital controls (lifted in 2017), and a focus on local industries. Unemployment hovers around 4%, with low income inequality and robust social welfare.
- Currency: Icelandic króna (ISK). Iceland is part of the European Economic Area but retains independence from the EU.
Key Economic Sectors
- Tourism: A significant economic engine, contributing 8–10% of GDP. Iceland attracts over 2 million visitors annually—more than five times its population.
- Fishing: Long the backbone of Iceland’s economy, fishing still accounts for a large portion of exports.
- Renewable Energy: 100% of Iceland’s electricity comes from renewable sources—mainly geothermal and hydropower.
- Tech and Startups: Reykjavik has a growing tech scene, particularly in fintech and biotech.
Currency: The Icelandic króna (ISK)
Politics and Governance
A parliamentary republic with a highly effective democratic system is Iceland.
Government Structure
Governance and Policies: Progressive and Green
Iceland’s parliamentary republic prioritizes sustainability and social equity.
- Environmental Leadership:
- Carbon Neutrality: Aiming for 2040, leveraging geothermal plants like Hellisheiði.
- Conservation: Over 20% of land is protected, including Vatnajökull National Park. Reforestation efforts combat centuries of deforestation.
- Social Policies:
- Universal Healthcare and Education: Free public healthcare (with nominal fees) and education up to university level.
- Immigration: Historically strict, now easing to address labor shortages in tourism and construction.
- Defense: No standing army; NATO membership since 1949. The Coast Guard oversees maritime security.
- President: A largely ceremonial head of state.
- Prime Minister: Head of government.
- Althingi: The world’s oldest surviving parliament was founded in Iceland in 930 AD.
Progressive Policies
- Universal Healthcare: Publicly funded, high-quality care.
- Education: Free at all levels, including universities.
- Parental Leave: One of the most generous systems globally, allowing both parents substantial leave.
- Environmental Protection: Ecosystems and natural resources are safeguarded by strict legislation.
Challenges
Despite its strengths, Iceland faces several challenges:
- Geographic Isolation: Increases the cost of goods and limits certain trade opportunities.
- Volcanic Risk: Eruptions can disrupt air travel and threaten infrastructure.
- Tourism Dependence: Over-reliance on tourism makes the economy vulnerable to global events (e.g., pandemics).
Why Iceland Stands Out
- Safety: One of the lowest crime rates in the world. Police officers rarely carry guns.
- Equality: Top-ranked in gender equality and LGBTQ+ rights.
- Environment: A model for sustainable energy and ecological preservation.
- Innovation: Outperforms its peers in artistic production, digital innovation, and scientific research.
Natural Wonders and Tourism: Beyond the Ordinary
Iceland’s geology is a tourist magnet:
- Volcanoes and Geysers: Recent eruptions (Fagradalsfjall, 2021–2023) and Strokkur geyser’s hourly bursts.
- Glaciers and Parks: Vatnajökull, Europe’s largest glacier, and Thingvellir, a UNESCO site where tectonic plates meet.
- Wildlife: Puffins, whales, and the iconic Icelandic horse—a purebred descendant of Viking steeds.
Infrastructure: The Ring Road (Route 1) circles the island, though rural roads may be unpaved. Reykjavik’s compact design fosters walkability.
Challenges: Balancing Growth and Sustainability
- Over-Tourism: Pre-pandemic influx strained infrastructure, prompting initiatives like the Icelandic Pledge for responsible travel.
- Economic Vulnerabilities: Reliance on tourism and fishing exposes volatility, as seen during COVID-19.
- Housing Shortages: Urban demand outpaces supply, particularly in Reykjavik.
Conclusion
Iceland is an intriguing example of how creativity, social cohesiveness, and environmental stewardship can lead to prosperity in a small, isolated nation. With its stunning landscapes, vibrant culture, and forward-thinking policies, Iceland continues to inspire countries far larger and more populous.
Whether you visit for the geothermal spas, the northern lights, or to explore the Icelandic sagas, one thing is certain—you’ll leave with a sense of awe for this unique and resilient island nation.